Technical Termonology - Piezo-Electric Device
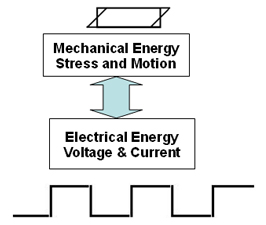
Quartz is kind of crystallized Silicon Dioxide (SiO2). The quartz crystal structure has the characteristics of piezoelectric effect (Fig.1), to exert pressure in the crystal in certain directions; the direction of the vertical force will produce electrical potential. Energy is converted between electrical and mechanical, millions of times per second. Hence, its characteristic is very different from other components.
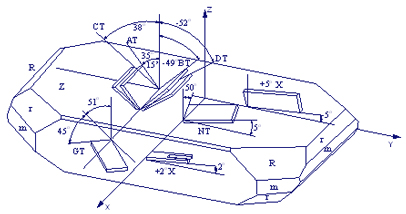
According to different cutting orientation with quartz bars, there are different kinds of quartz plates such as AT, BT, CT….. –cut plates, which will determine the characteristic of quartz crystal device. Cutting orientation process determines:
Quartz Crystal: Unit’s characteristics depend on the cutting orientation (Fig.2)
Tuning Fork: KHz Frequency level, such as 32.768KHz
AT-Cut type: MHz frequency range, such as 12MHz, 26MHz, 125MH
SAW type: Frequency range from MHz to GHz
 |
 |
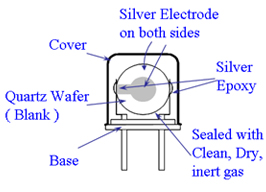
| (Fig.1) Typical Structure of HC-49U and SMD Quartz Crystal | (Fig.2) Cutting Orientation of Quartz Crystal |
 |
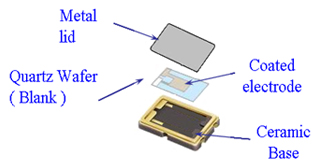 |
| (Fig.3) HC-49U Crystal | (Fig.4) SMD-Crystal |
Equivalent Model of a Quart Crystal
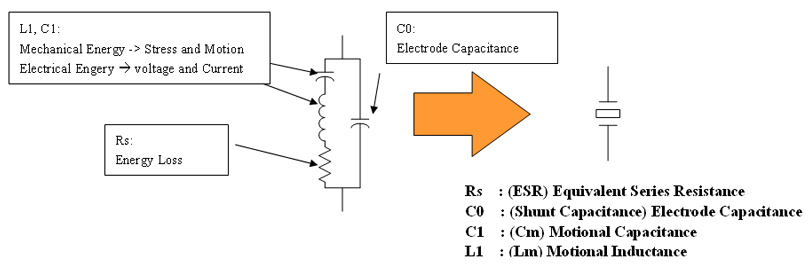
Raw Parameters of Crystal
Rs, C0, C1 and L1 give you all the information concerning impedance change of a crystal near by it operating frequency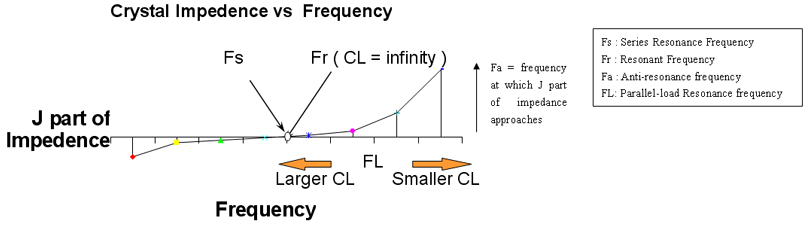
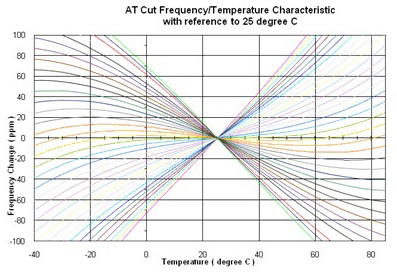
| Temperature Characteristic AT Cut For AT Cut, usually +/- 30 to 50 ppm over -10 to +60 Always refer to 25 degree C as 0 ppm |
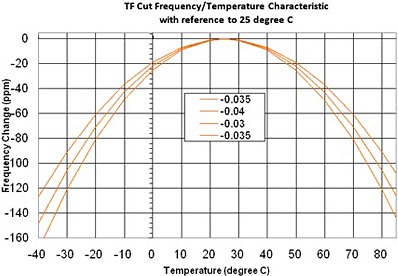
Temperature Characteristic Tuning Fork For Tuning Fork usually over 200 ppm Common habit is to refer to 25 degree C as 0 ppm Consider seriously to allow +80ppm typical for 25 C |
 |
 |
| Tuning Fork | AT-cut | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | kHz | MHz |
| Standard consumption | 02.uW | 50uW |
| ESR | Large | Less than TF |
| Temperature characteristic | Large tolerance Deviation than AT -cut | |
| Fundamental | Overtone | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency (AT Cut) | 4MHz to 50MHz (Depend on application) | 18MHz to over 100MHz |
| ESR | Lower ESR | Higher ESR |
| Drop Shock Performance | The higher the frequency, the worst the drop shock | Better due to much thicker blanks |
| Pullability | Can be designed for FM, PLL, VCO applications | Very High Q, hence frequency less dependent on other component variations. |
| Circuit Design | Usually does not require filter to precent crystal oscillating at its overtones | Usually requires filters to prevent crystal oscillating at its fundamental frequency |